 Mobile Tips
Mobile Tips
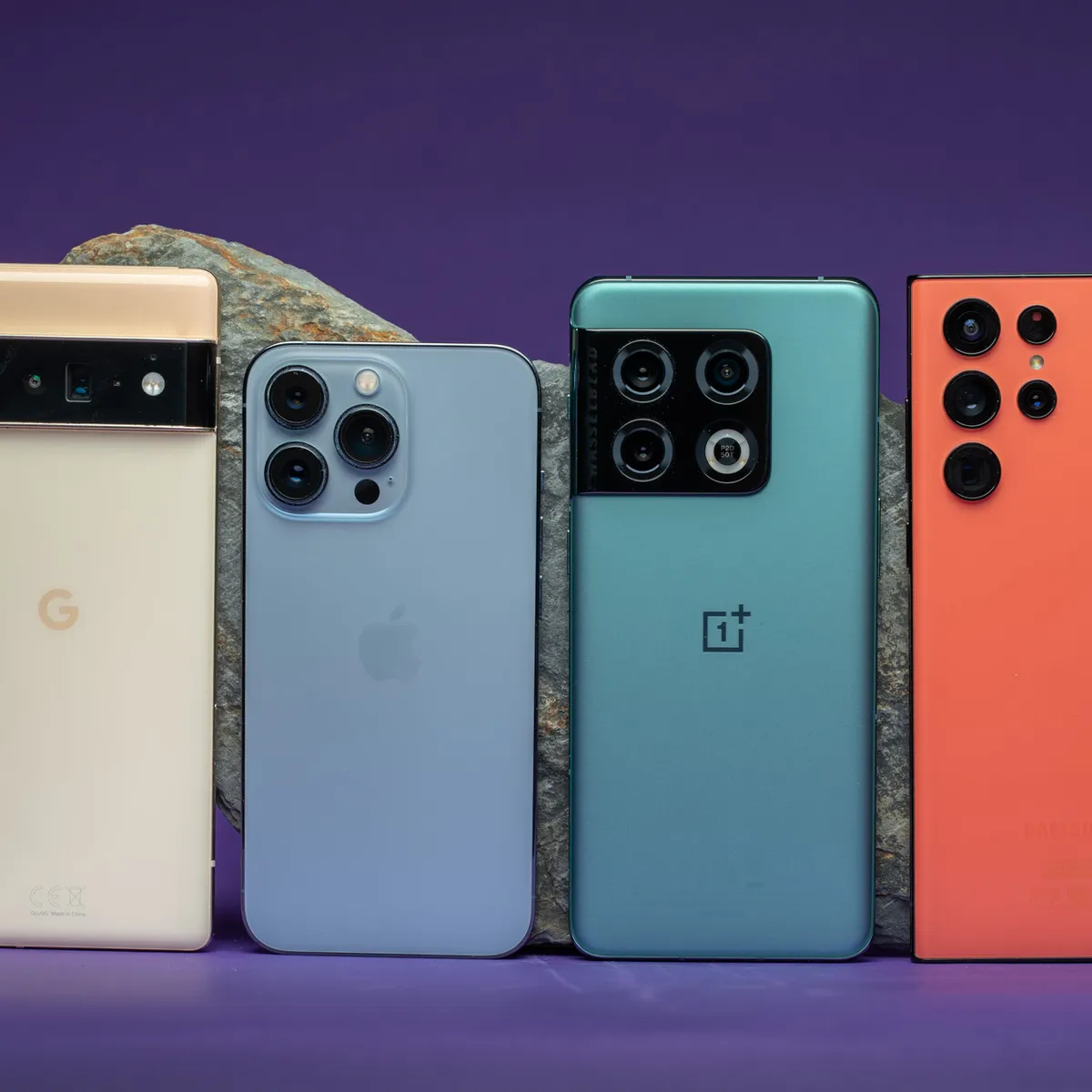
రూ. 15,000 లోపు లభించే బెస్ట్ 5G స్మార్ట్ఫోన్లు (2025)
మీరు కొత్త 5G ఫోన్ కొనాలని అనుకుంటున్న
Read MoreStay ahead with in-depth gadget reviews, breaking tech news, and expert analyses. The ultimate hub for technology enthusiasts.
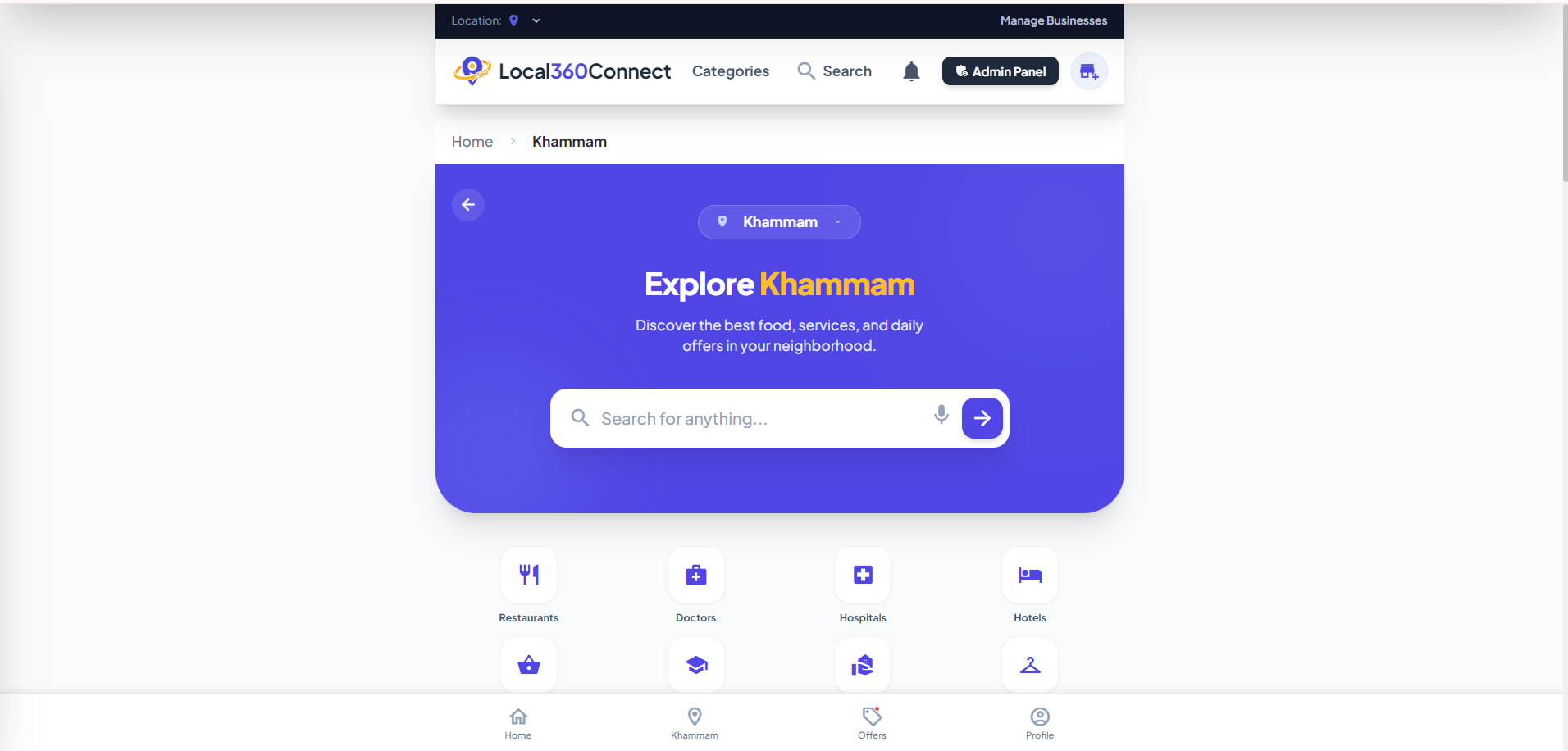 Featured
Featured
Local360Connect is your hyperlocal business discovery platform built to connect people with trusted local shops, services, and professionals — s...
Read Full ReviewBreaking stories and updates from the technology world.
 Mobile Tips
Mobile Tips
మీరు కొత్త 5G ఫోన్ కొనాలని అనుకుంటున్న
Read More Business Tech
Business Tech
Global AI firm Anthropic has officially inaugurated its first office in India in Bengaluru, marking
Read More Technology News
Technology News
Local360Connect is your hyperlocal business discovery platform built to connect people with trusted
Read More Gadget Reviews
Gadget Reviews
Best Cheap Home Projector 2024 – Portronics Beem 440 Review Looking for a budget-friendly h
Read MoreWelcome to the #1 Telugu Tech Platform. We are here to serve you.
Read More